Most extensions occur in the motive waves of impulses. Generally, an extension is an extended impulse structure with enlarged waves inside, which are almost the same height and length as the other waves of the impulse. So, if a usual impulse has a five-wave structure, an impulse with an extension in one of the motive waves subdivides into nine waves.
Where do extensions occur?
Extensions only occur in motive waves: the first, third and fifth wave of an impulse. Most impulses only have an extension in one of the motive waves, most commonly in the third wave. From time to time, you might encounter two extensions inside a single impulse, but that's rare. Also, during a long and strong trend, it's possible to have an extension inside another extension - that’s called a multi-extension.
The extension and other waves of the impulse
If a third wave forms an extension, then the fifth wave will likely be the same as the first wave. If the first and the third waves are of about equal amplitude, the fifth wave could be extended. It's impossible to have an extension in both waves one and five, because then wave three would be the shortest, which would violate the definition of an extension.
Sometimes, it can be difficult to choose the right scenario to focus on as the main one. If all the motive and corrective waves are nearly the same, you may not have many places to look for an extension. The best thing to do in this situation is pick a wave scenario with a relatively modest prediction. Try to look for extensions in third waves to give yourself the best chances.
The extension and correction patterns
As you already know, there can only be an extension in the motive waves. However, sometimes it’s possible to observe something like an extension inside a zigzag. In these cases, one of the motive waves (A and C) of the pattern is much longer than another. There’s no mention of extensions inside zigzags in the book “The Elliott Wave Principle: A Key to Market Behavior”, but sometimes such a disproportion between waves A and C takes place.
Examples
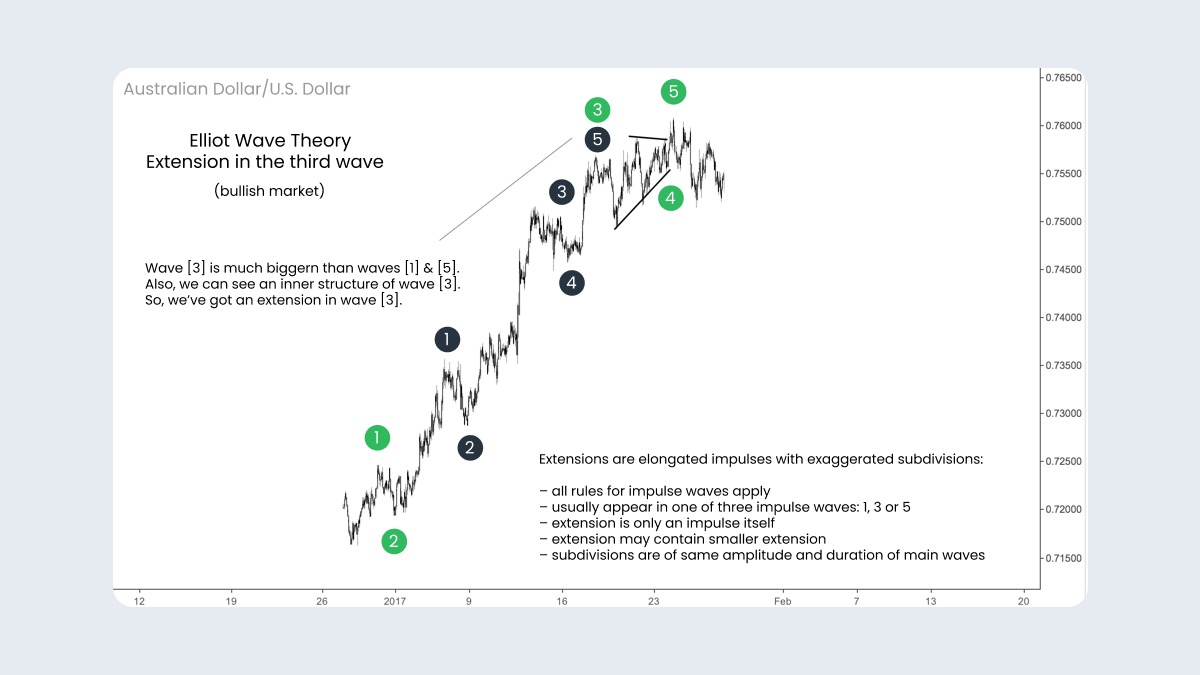
Extension in the third wave
The chart below represents an impulse with a huge extension in wave ((3)), which subdivides into five waves that are very similar to waves ((1)), ((2)) and ((5)). As you can see, after wave ((4)) we had a tiny price movement in the fifth wave. In most cases, it’s likely that if your third wave is more than a 1.618 multiple of your first wave, there’s a green light for a relatively small fifth wave.
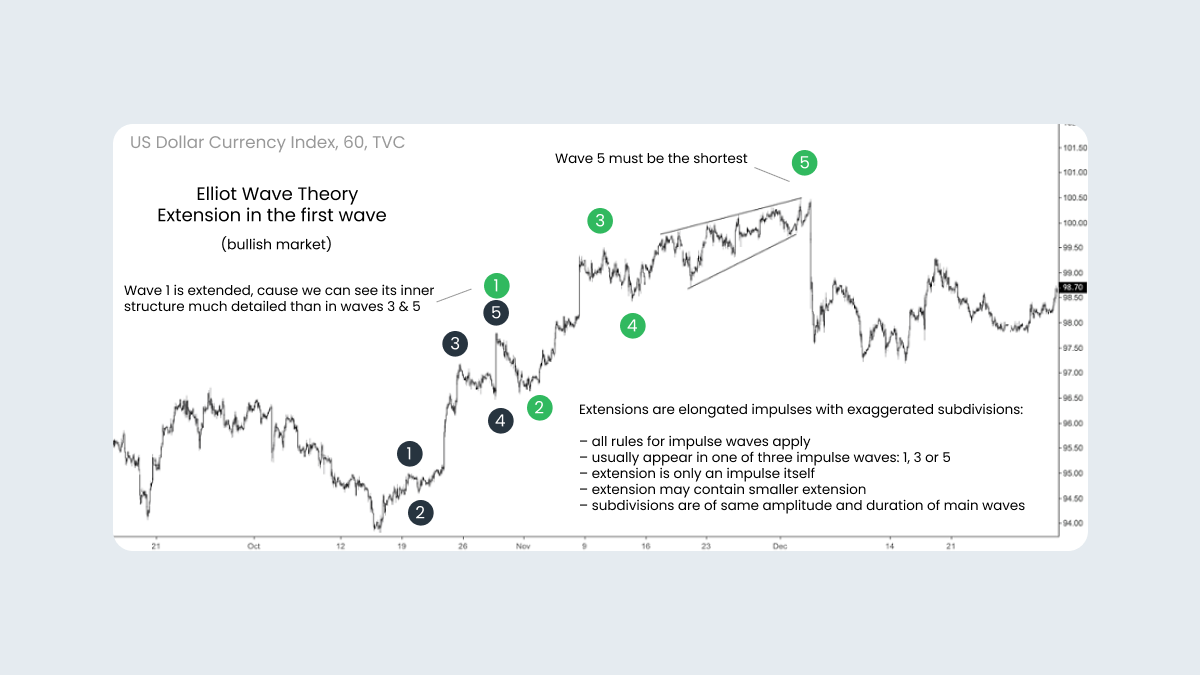
Extension in the first wave
Sometimes, the fifth wave of an impulse forms an extension - this occurs during massive market rallies. On the next chart, wave (1) could be the fifth wave itself, so only a three-wave decline and the subsequent pullback point out that the extension has started. Moreover, a triangle in wave (4) confirms that there’s a developing impulse from the ending of the fourth wave. Thus, we should be extremely careful with fifth-wave extensions when counting waves in real-time.
Inside the five-wave advance: what to watch for
A first-wave extension doesn’t form often. The next example shows a five-wave advance with the longest first wave. Keep in mind: if the first wave is extending, the third wave is usually smaller than the first wave. In that case, the vast majority of the time, an impulse with an extended first wave usually has the shortest fifth wave. The third wave can’t be the shortest.

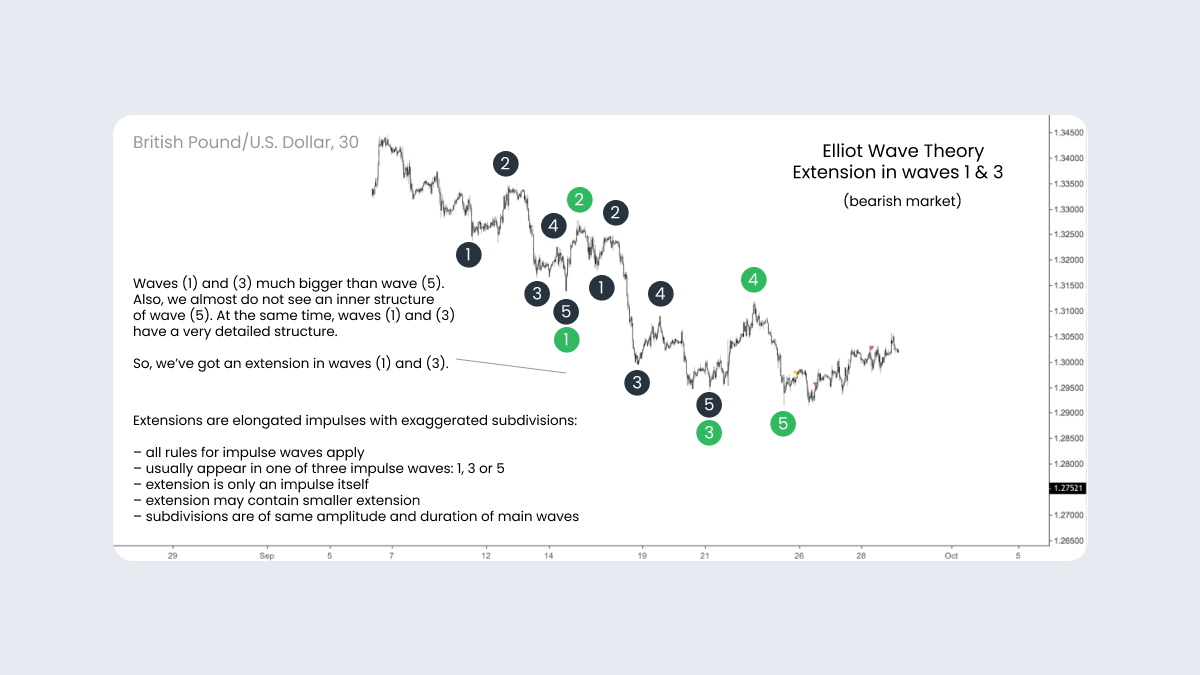
The extension in first and third waves
It is also possible to have an extension on both waves one and three of an impulse, as shown on the following chart. The first and third waves are much bigger than the fifth wave. Also, the first and third waves have a very detailed structure, but the fifth wave doesn’t.
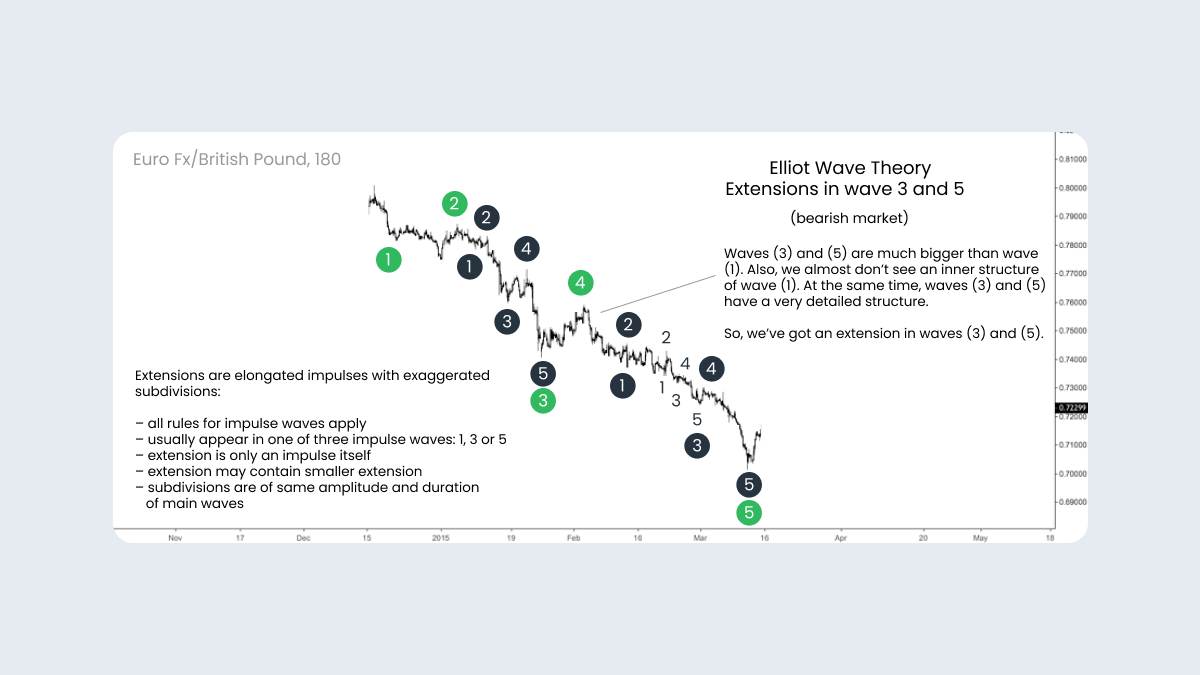
The extension in third and fifth waves
Another option is an extension in both the third and fifth wave. This usually happens during a strong and long trend. As shown on the next chart, the first wave is small, while the third and fifth waves are huge and we can see all the subdivisions of these impulses.
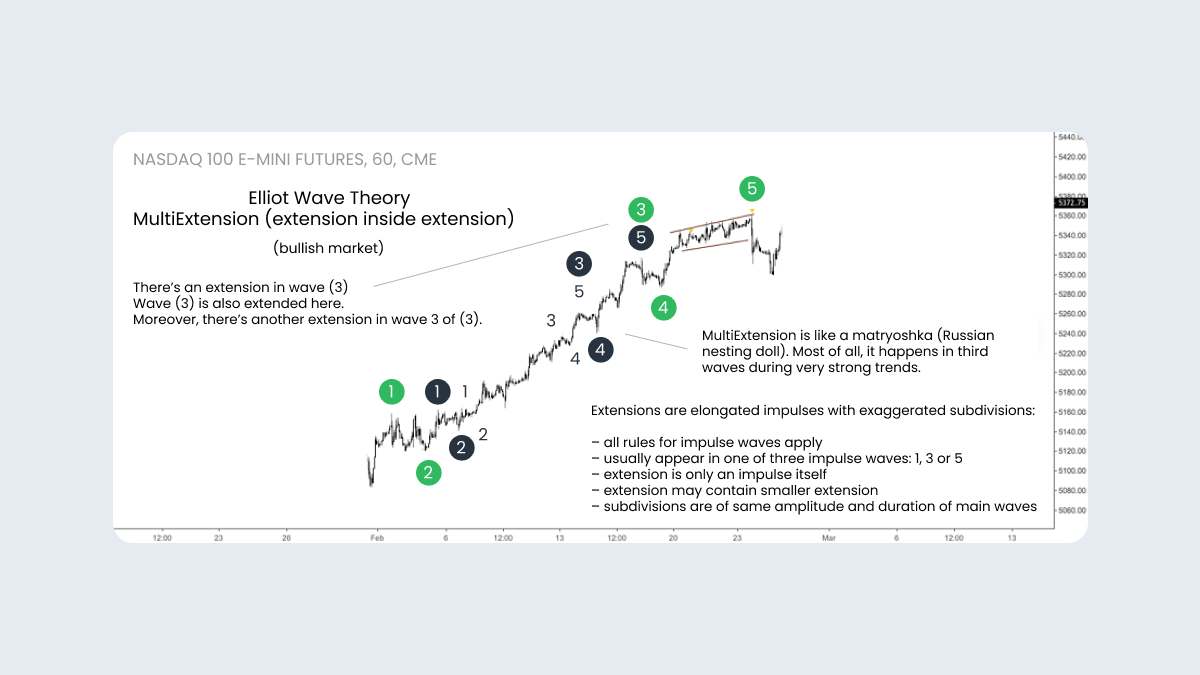
The multi-extension
The trickiest type of extension is the multi-extension. It usually forms on the stock market. During a multi-extension, we see a lot of similar waves, so sometimes it’s pretty hard to do a wave count. The key to recognizing a multi-extension is a series of corrections, which form, smaller and smaller, one after another. If this happens, you could predict a multi-extension; but at the same time, it’s advisable to try to find alternate wave counts with fewer expectations. By doing this, you could also find the critical levels, which are supposed to be red lines for a wave count with a multi-extension.
Summary
Extensions are an essential part of impulse waves. They happen all the time on all the markets. In terms of trading, extensions bring the most interesting opportunities; but we should always remember to keep risks at a reasonable level.